

The SCPT alloy is ultrafine-grained cemented carbide that was independently developed by Nippon Tokushu Goukin Co., Ltd. The name SCPT is derived from the initials of "ultrafine-grained cemented carbide by pinning effect of Ti(C,N)." Unlike conventional methods, this alloy inhibits WC grain growth through the pinning effect of superfine-grained Ti(C,N). Compared to conventional materials, the SCPT alloy is high hardness, strength, and wear resistance.

The SCPT logo is hexagonal, reflecting the crystal structure of WC. It incorporates indigo blue, a traditional Japanese color, to represent our company‘s(Japan) invention. The red circle indicates the pinned Ti(C,N) particles.
※SCPT is a registered trademark of Nippon Tokushu Goukin Co., Ltd.
※PAT.6227517、 PAT. 7383498
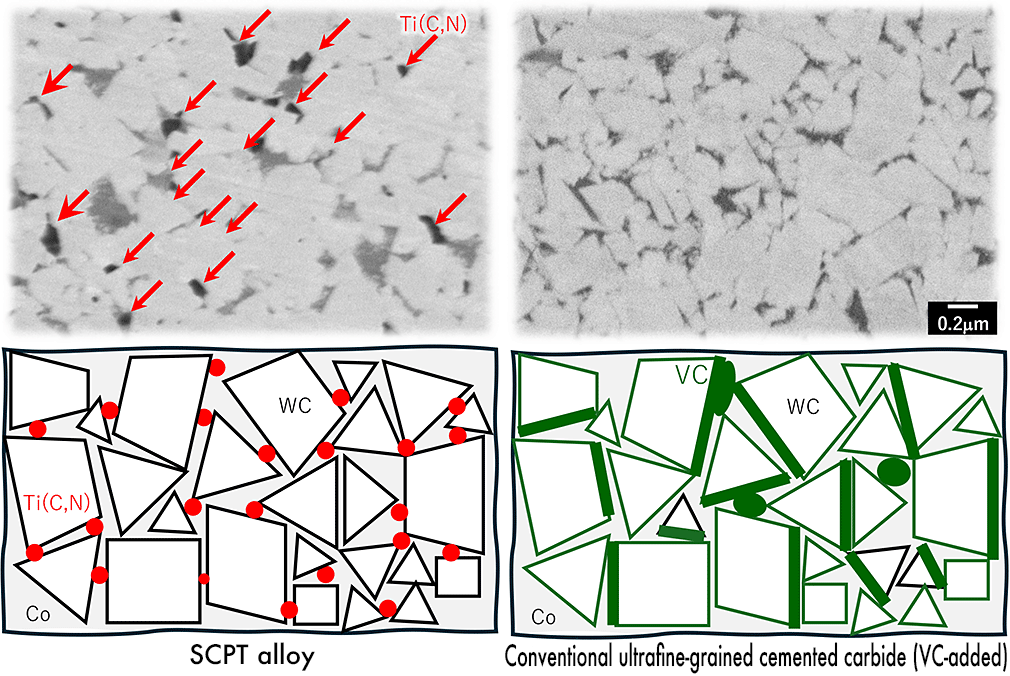
The SCPT® alloy contains fine Ti(C,N) particles dispersed among the WC grains. This inhibits WC grain growth. The result is high strength and excellent wear resistance. Conversely, conventional ultrafine-grained cemented carbide experiences reduced strength and wear resistance because VC exists at segregation sites and WC/Co interfaces.
| Material name |
WC grain Size µm |
Content of Co wt% |
Bending strength GPa |
Hardness HRA |
Applicable tool types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S6 | 0.4 | 6.0 | 4.4 | 94.2 | Cutting tool |
| S10 | 0.4 | 10.0 | 4.7 | 92.7 | Cutting tool |
| SH6 | 0.4 | 6.0 | 3.6 | 94.7 | Cutting tool |
| SH8 | 0.4 | 8.0 | 3.8 | 94.0 | Wear-resistant tool |
| SH10 | 0.4 | 10.0 | 4.3 | 93.4 | Cutting tool |
| Workpiece material | Drill | End mill | Reamer | Insert |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon steel · Alloy steel | ○ | ○ | ◎ | ○ |
| Stainless steel | ○ | ○ | ◎ | |
| Cast iron · Ductile iron | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| Aluminum alloy | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | |
| High-hardness steel | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ |
This classification is based on actual performance, which may vary depending on usage conditions.
This tool demonstrates outstanding performance in machining cast iron, ductile iron, aluminum alloys, and high-hardness steel. Among tool types, it achieves exceptional tool life particularly with reamers.
| Mold Type | Applicable |
|---|---|
| Powder molding die | ◎ |
| Drawing die | ○ |
| Pull-out plug | ○ |
| Cutting blade | ○ |
| Impact-resistant mold | ✕ |
This classification is based on actual performance, which may vary depending on usage conditions.
We have a proven track record of extending mold life, especially for high-hardness powder forming in powder molding dies.
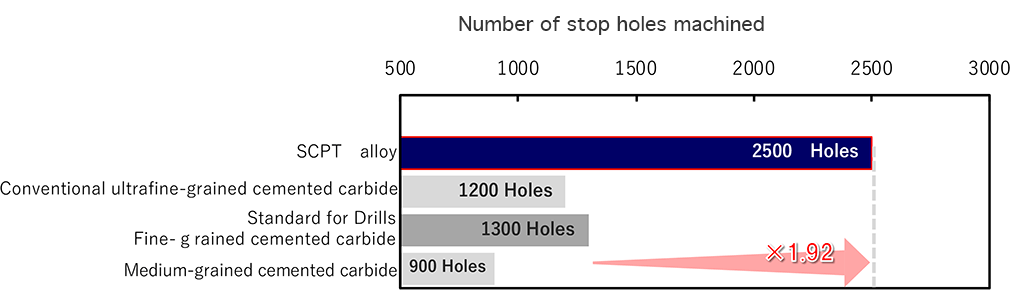
The SCPT® alloy has a longer tool life than other materials because it has fewer fine defects at the cutting edge in the initial stage.
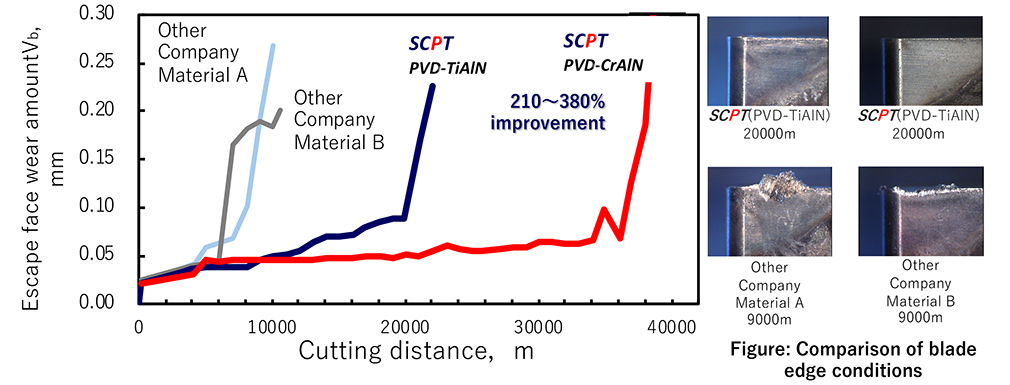
The SCPT® alloy enables stable machining due to minimal initial edge chipping, contributing to improved tool life.
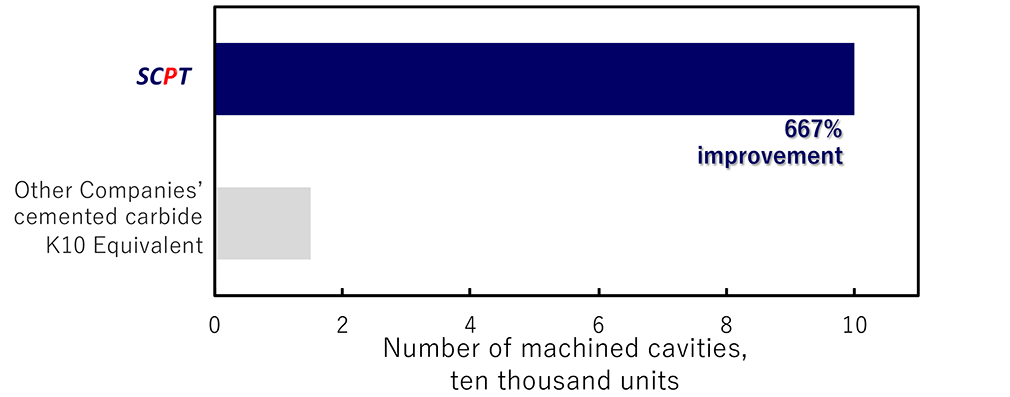
The SCPT® alloy significantly extends the service life of cutting tools by reducing edge wear and chipping during aluminum alloy machining compared to tools using other carbide alloys.

The SCPT® alloy contributes to extending the service life of cutting tools in ductile iron (all cast iron).
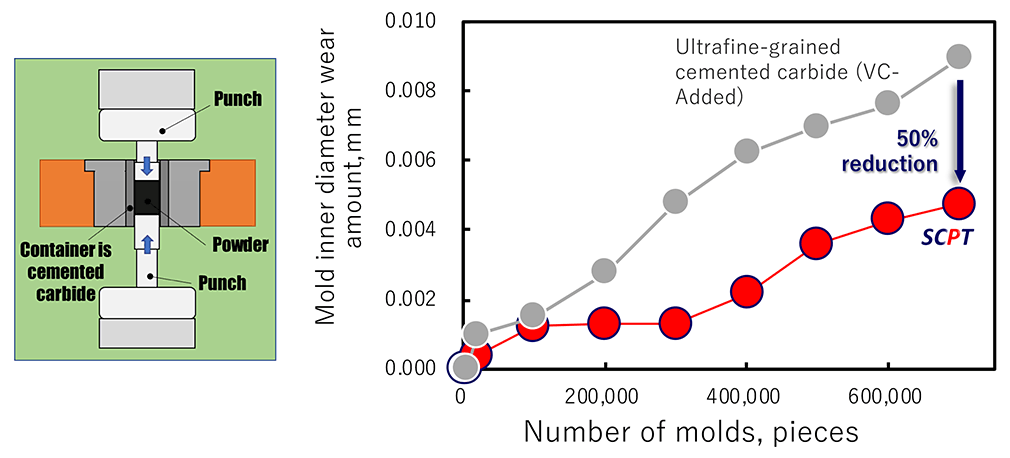
Compared to conventional ultrafine-grained cemented carbides, the SCPT® alloy offers superior wear resistance, resulting in slower mold wear progression and extended mold life.

To request an the SCPT® Alloy catalog, please contact us via “contact us”.